Streamlining Global Trade: The Key Role of Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) Service and IOR Numbers
International trade is the lifeblood of the global economy, connecting businesses across borders and providing consumers with an array of products from around the world. However, behind the scenes, trade involves a labyrinth of regulations, customs processes, and crucial terms like Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) Service and IOR Numbers, or Importer of Record Numbers. In this article, we will uncover the significance of DDP service and IOR Numbers in simplifying global trade operations.
Deciphering Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) Service
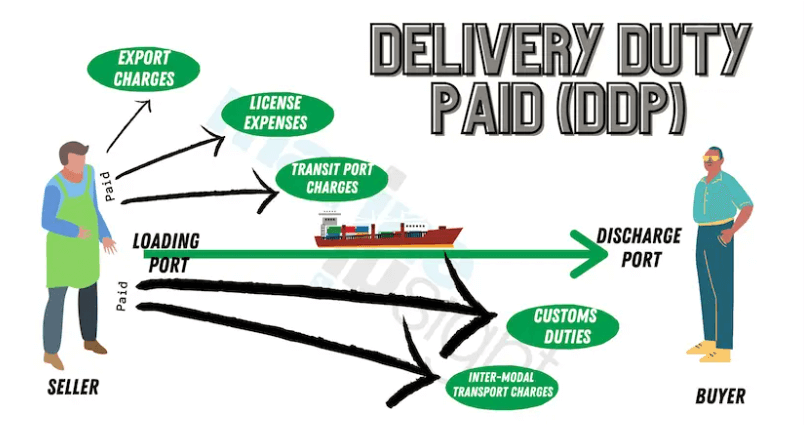
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) is an internationally recognized trade term within the Incoterms framework. This term denotes that the seller is responsible for delivering goods to the agreed-upon destination, cleared for import, and liable for all applicable duties, taxes, and fees. The Delivered Duty Paid service offers several advantages for both importers and exporters, making it a preferred choice for many international transactions:
1. Importer’s Ease:
- Cost and Risk Management: One of the key benefits for importers is that DDP service simplifies the buying process. The seller takes on the responsibility of all shipping processes and related expenses, sparing the buyer from the complexities of customs clearances, duties, and taxes.
- Transparent Costs: DDP provides a clear, comprehensive overview of the total shipment cost, encompassing not only the product’s price but also all costs related to shipping and customs clearance.
2. Seller’s Obligations:
- Shipping and Delivery: The seller arranges transportation of goods and ensures their secure delivery to the agreed-upon destination.
- Customs Compliance: The seller manages import/export documentation, ensuring compliance with customs regulations and making the necessary payments for import duties and taxes.
The Crucial Role of IOR Numbers
In the context of DDP service, the IOR Number, or Importer of Record Number, emerges as a critical element. This unique identifier is assigned to the entity responsible for importing the goods into the destination country and plays a pivotal role in ensuring compliance with customs and tax regulations, facilitating record-keeping, and streamlining international trade:
1. Legal Requirement:
- Mandatory Compliance: Many countries require businesses engaged in international trade to obtain an IOR Number. It signifies that the importer adheres to the customs laws and regulations of the destination country.
2. Simplified Documentation:
- Efficient Customs Clearance: The presence of an IOR Number expedites customs clearance processes, enabling customs authorities to quickly identify the responsible party.
- Effective Record-Keeping: IOR Numbers are instrumental in maintaining comprehensive and organized records of imported goods, including details such as origin, destination, and value. This proves invaluable for audits, tracking, and compliance.
3. Taxation and Duty Calculation:
- Accurate Tax Reporting: IOR Numbers are often linked to tax reporting, ensuring that tax authorities can precisely assess and collect the relevant import duties and taxes.
Implementing DDP Service and IOR Numbers in Practice
Consider a practical scenario where a business in Country A is procuring products from a supplier in Country B, with the destination being Country A. The supplier in Country B agrees to provide DDP service, taking responsibility for delivering the products to the buyer’s doorstep in Country A.
In this case, the supplier from Country B secures an IOR Number for the buyer in Country A, designating them as the importer of record. This IOR Number is then used throughout the shipping process, ensuring compliance with customs regulations in both countries.
Effective Strategies for Using DDP Service and IOR Numbers
To successfully engage in international trade with DDP service and an IOR Number, consider the following best practices:
1. Clearly Defined Agreements:
- Ensure that all responsibilities and costs related to DDP service are explicitly detailed in the sales contract or agreement between the buyer and seller.
2. Reliable Partners:
- Collaborate with reputable suppliers, carriers, and customs brokers who are well-versed in the requirements and regulations governing DDP shipments.
3. Meticulous Documentation:
- Maintain accurate records and ensure all necessary documents, including invoices, packing lists, and customs documentation, are in order.
4. Stay Informed:
- Keep abreast of changes in customs regulations and tax laws in both the exporting and importing countries to avoid unforeseen delays or costs.
Conclusion
Delivered Duty Paid (DDP) service and the IOR Number (Importer of Record Number) are vital components of international trade. They provide transparency, compliance, and efficiency to cross-border transactions, benefiting both buyers and sellers. By understanding the role of DDP service and the significance of the IOR Number, businesses can confidently navigate the complexities of global trade. With DDP and the IOR Number, international trade becomes more accessible, manageable, and profitable than ever before.



