What Are The Parts Of The Nervous System?
The nervous system is one of the most essential organ systems in our body. It comprises the brain, spinal cord, and nerves throughout the body. It is responsible for all voluntary and involuntary actions. The nervous system takes the stimulus and generates a suitable response with the help of neurons and neurotransmitters.
Here’s everything you need to know about the nervous system and its parts in detail.
What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system translates to the system of nerves. Nerves arise from the brain and spinal cord and carry sensory and motor information throughout the body. They comprise neurons that are the building blocks of nerves that you can easily observe under an electron or optical microscope.
What are Neurons?
Neurons are the basic unit of the nervous system that make up the nerves. A neuron consists of a nucleus, cell body, dendrite, axon, axon terminal, synapse, the direction of impulse, Myelin sheath, and Node of Ranvier.
Dendrites are tree-like extensions at one end of a neuron that contribute to increasing the surface area of the cell body. They receive information and transmit electrical impulses to generate a response. On the other hand, axons are thin fibers extending from the neurons that help transmit electrical signals through sensory movement. Myelin sheath provides protection and ease of transmission to axons.
Parts of the Nervous System
There are two major parts or classifications of the nervous system
- Central Nervous System
- Peripheral Nervous System
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system comprises the brain and spinal cord, which act as the primary location of the exchange of information in the body. They analyze the stimuli and produce a response as needed. The central nervous system is made up of the brain and spinal cord.
Brain
The brain is a complex organ that controls motor skills, thought, emotion, memory, hunger, temperature, breathing, vision, and other processes that regulate the body. It is responsible for processing sensory information and coordinates voluntary and involuntary body functions.
It also helps maintain the body’s balance, temperature, sleep-wake cycle, and water needs and regulates every organ system. The brain consists of three regions; the forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain.
Forebrain
The forebrain is the front-most part of the brain that processes information regarding complex cognitive tasks. It is involved in voluntary motor skills, sensory functions, critical thinking, speech, etc. It also regulates homeostasis, including temperature, pleasure, pain, blood pressure, and thirst.
Midbrain
The midbrain is present between the forebrain and hindbrain and acts as a connection between the two. It also connects the brain to the spinal cord, regulating eye movement and sound interpretation.
Hindbrain
The hindbrain manages the heart rate, respiration, blood pressure, alertness, and sleep. It also contributes to involuntary reflexes such as swallowing and sneezing.
Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is a long tube-like structure that runs from your brain to your lower back and facilitates the transmission of signals. It can control simple reflexes without transmitting it to the brain. The spinal cord is responsible for carrying signals that enable you to feel sensations and move.
Peripheral Nervous System
The other part of the nervous system is the peripheral nervous system. It is composed of nerves that transmit signals from the body organs to the CNS and vice versa. The PNS is categorized into the autonomic and somatic nervous systems.
Autonomic Nervous System
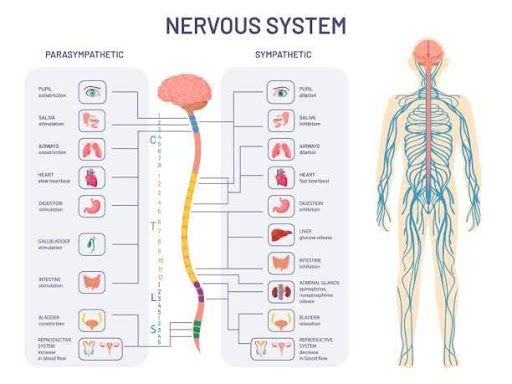
The autonomic nervous system comprises neurons that connect the CNS and the internal body organs. It regulates involuntary body actions and physiological processes like respiration, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, etc. There are two types of the autonomic nervous system; sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system.
Sympathetic Nervous System
The sympathetic nervous system is known for its fight-or-flight response. It comes into action during emergency or stress conditions when your body needs an immediate response.
Parasympathetic Nervous System
The parasympathetic works in contrast to the sympathetic nervous system and works to conserve energy. It helps regulate body functions like digestion and urination besides conserving energy during sleep when the body relaxes.
Somatic Nervous System
The somatic nervous system consists of nerves that send information to and from the muscles, senses, and the spinal cord. They comprise afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) nerves that carry information.
The Bottom Line
The nervous system is the fundamental system of the body that regulates all body functions. It comprises the central nervous system and the peripheral nervous system. The central nervous system consists of the brain and spinal cord, whereas the nerves make up the peripheral nervous system. They work together to ensure proper voluntary and involuntary movements with the help of the somatic and autonomic nervous systems.
FAQs
What are the 4 major organs of the nervous system?
The major nervous system components are the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs, and nerves.
What are the divisions of the nervous system?
The nervous system is divided into four primary categories, including the cranial, central, peripheral, and autonomic nervous systems.
What is the basic unit of the nervous system?
A neuron is the basic unit of communication in the nervous system. The neurons (nerve cells) consist of the dendrite, axon, and the cell body.








