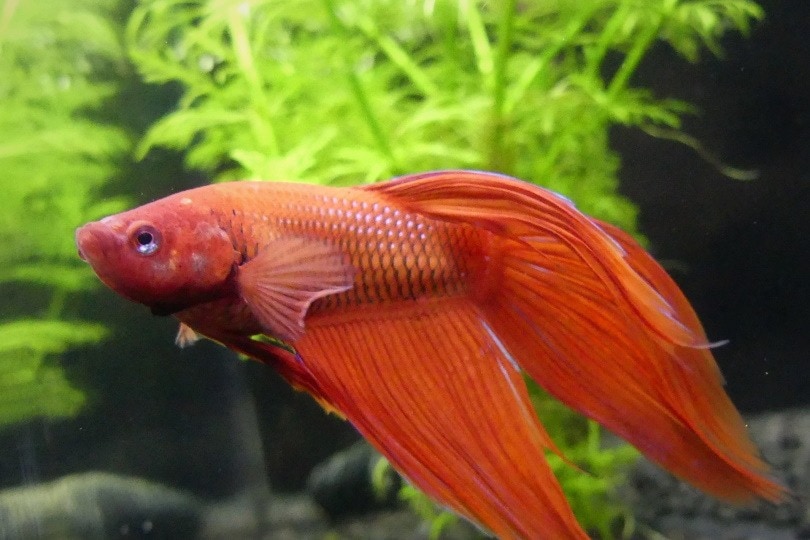
Do Betta Fish Have Teeth?
Betta fish, also known as Siamese fighting fish, are popular aquarium fish known for their vibrant colors and aggressive behavior. Betta fish are carnivorous, and they have teeth to help them catch and eat their prey. Betta fish teeth are small, sharp, and pointed inwards, and they are located in the front of the mouth.
The directions of the betta fish teeth are crucial for their feeding behavior. The teeth are angled inwards, allowing the fish to grasp and hold onto their prey, such as insects, crustaceans, and small fish. Once the prey is captured, the betta fish will use its sharp teeth to tear it apart into bite-sized pieces.
Betta fish have a unique feeding behavior known as “gulping.” This involves the fish quickly sucking in water and food, which then passes over the teeth, allowing them to grab onto the prey. The teeth also help the betta fish to grind up their food before swallowing it.
The direction of the betta fish teeth is essential for their survival in the wild. In their natural habitat, betta fish face various challenges, including competition for food and predators. The teeth allow them to catch and consume their prey quickly, which is vital for their survival.
The directions of the betta fish teeth play a significant role in their feeding behavior and survival. Understanding this unique feature can help aquarium enthusiasts provide the appropriate diet and care for their betta fish to thrive.
Number of Teeth of the Betta Fish
Do betta fish have teeth? Betta fish have a unique set of teeth that are different from those found in most other fish species. Betta fish have small, needle-like teeth called cordiform teeth, which are located in their jaws and on the roof of their mouths. These teeth are used primarily for gripping and holding prey items, such as insects and small crustaceans, which the betta fish feeds on in the wild. Betta fish do not have molars or other types of teeth that are used for chewing or grinding food, as their diet consists mainly of small, soft-bodied prey that can be swallowed whole. In total, betta fish have around 30 cordiform teeth in their mouths.
Life Cycle of the Betta Fish Teeth
Betta fish have a unique set of teeth that undergo a continuous life cycle throughout their lifespan. Betta fish teeth are called pharyngeal teeth and are located in the back of their throat.
The life cycle of betta fish teeth begins with the growth of new teeth. Betta fish continuously produce new teeth throughout their lives. As their old teeth wear down or fall out, new teeth grow to replace them. This process ensures that betta fish always have a full set of functioning teeth to help them catch and eat their prey.
The rate of tooth growth varies depending on the betta fish’s diet and environment. A diet rich in protein and calcium can accelerate tooth growth, while poor water quality and a lack of nutrients can slow it down.
As betta fish age, their teeth may become worn down or damaged. If this happens, the old teeth will fall out and be replaced with new ones. This process is essential for maintaining healthy and functional teeth throughout their lifespan.
The life cycle of betta fish teeth is continuous and essential for their survival. As they grow and age, their teeth continuously regenerate to ensure that they have a full set of functional teeth to help them eat and survive in their environment. It is crucial for betta fish owners to provide their fish with a healthy diet and environment to ensure proper tooth growth and maintenance.
Do the Teeths of Betta Fish Have Regenerating Power?
The most important question is do betta fish have teeth? Betta fish are like all living creatures, betta fish are susceptible to injuries and diseases that can affect their health and well-being. One question that often arises among betta fish owners is whether the teeth of betta fish have to regenerate power.
The short answer is no, betta fish teeth do not have regenerating power. Unlike some other species of fish, betta fish teeth are not constantly growing or regenerating. Once a betta fish loses a tooth, it is gone for good.
That being said, betta fish are able to adapt to tooth loss by adjusting their diet and chewing habits. They may also develop new ways of catching and consuming their food. However, it is important for betta fish owners to monitor their fish for signs of dental problems, such as difficulty eating or unusual behavior, and seek veterinary care if necessary.
In summary, while betta fish teeth do not have regenerating power, these resilient fish are able to adapt to changes in their dental health with proper care and attention.