What’s The Difference Between PCB and PCBA?
Electronic systems are the heart of any electro-mechanical device. These deliver the power that a system needs to function in the best possible way. At the heart of these complex systems is the Printed Circuit Board (PCB). This is the main device that is used to deliver electricity to a range of different components. These components have many functions that define how the device being driven by the PCB works.
These boards and components are usually known by the term Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA). This makes a unique difference between the two design forms. This means that a PBCA is an assembly of a PCB and a collection of electronic components that are attached to it. Before a PCBA can exist, a PCB must first be manufactured. What’s The Difference Between PCB and PCBA? For more information.
What is a PCB?
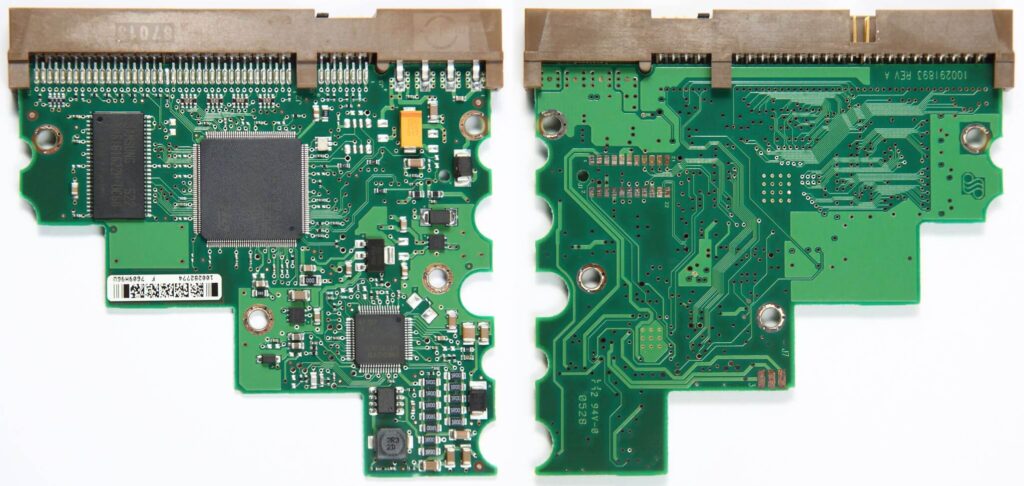
The PBC is the most basic part of the PCBA, but is useless without the added components. But to ensure that the components are fitted in the correct positions, the PCB needs to be suitably marked to show this. By definition, PCBs are the basic building blocks of electronics made today. PCBs are made of laminate materials like fibreglass or composite epoxy. They hold components in place and connect them physically. As the PCB design says, the board is printed and etched with conductive paths that connect the different electronic parts. PCBs can have many forms:
- Single Layer. Single-layer PCBs are often called single-sided boards, and they have components on one side only. They only have one layer of copper, which makes them conduct electricity. A single-layer board has a supportive base, a layer of conductive metal and a silk screen for protection and component placement. Single-layer boards are used in a lot of simple electronic products.
- Double layer. PCBs with two layers have twice as many layers as a single-layer board but less than a multi-layer board. Both single-sided and double-sided PCBs have a single layer called the substrate. The difference is that with double layer boards, both sides of the base have a layer of metal that conducts electricity.
- Multi-layer. Multi-layer PCBs are made by stacking three or more double-sided boards on top of each other. They can hold as many boards as the PCBA needs to work correctly. PCBs with more than one layer are usually used in more complicated systems that need a lot of connections. Each layer can communicate to each other through the conductive lines.
These are plain boards with conductive lines fixed on them. To make them workable as an electronic device, they need to have components added. You are looking for a PCB manufacturer that can make plain boards with conductive lines. These are called blank PCBs or bare PCBs.
What is a PCBA?
In contrast to a PCB, which is a blank board, a PCBA is a finished PCB assembly. It just needs all its electronic parts to be attached for it to work the way it was meant to. PCBA can also mean the process of putting together the board with all the important electrical parts. PCB assembly is done by makers in two main ways these days:
- Surface-Mount Technology. This is the most common method for making PCBs. As the name suggests, SMT uses solder paste to connect parts directly to the surface of the PCB. No holes need to be made in the board. This method makes it possible to place components on both sides of the board. This lets more components fit on a single board and makes PCBs smaller.
- Through-hole technology. This method runs the leads of the parts through holes that have already been drilled in the PCB. This style is not used as often as Surface Mount, but it is known for its dependability and durable connections. In some cases, boards put together with this method can handle more vibration and stress than boards put together with SMT.
- Mixed technology. As the name implies, mixed technology board assembly is a mix of both SMT and through-hole features. These assemblies are often used in a variety of situations that might need a mix of both kinds. This setup also doesn’t use solder paste, which makes it an important step for some uses.
- Cost of PCBs vs PCBA’s
There are many things that affect how much it costs to put together printed circuit boards. These include manufacturing costs, tooling costs, setup costs, turnaround time, number, and technology. Of course, the cost also depends on the parts, and the total cost of your PCBA can change based on where it’s made. It is important to think about how to ship and package the item.
The initial prices of labor include both human labor and factory work done by machines. Some countries may have cheaper wage costs, but they may have different standards for the quality of the work. Custom shapes and builds will also add to the total work costs. These set-up costs will not be needed for standard PCB designs.
Turnaround time and amount can be affected by things like the time of year, the country, how the product is made, what the customer wants, and more. Faster shipping and more work time will always cost more, and the cost of goods can change depending on a number of economic factors.



