Unveiling the Boundless Potential of 3D Scanning Services: Redefining Industries
In recent years, the field of 3D scanning has undergone tremendous advancements, revolutionizing industries across the globe. This cutting-edge technology has opened up new possibilities in various sectors, ranging from architecture and engineering to healthcare and entertainment. In this article, we will delve into the world of 3D scanning services, exploring its unique applications and the transformative benefits it brings to different industries.
Understanding 3D Scanning: A Brief Overview
What is 3D Scanning?
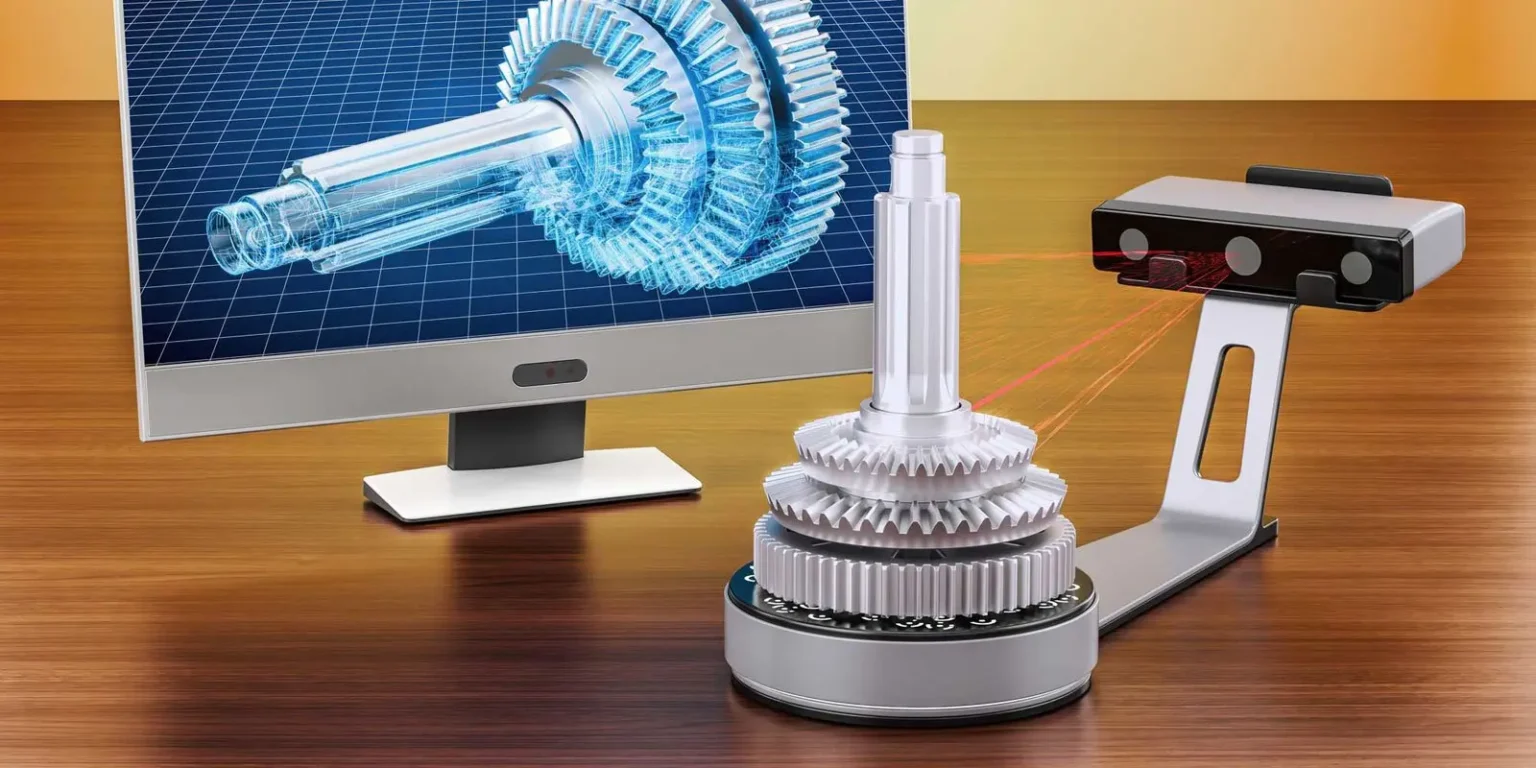
3D scanning is a process that involves capturing the shape, size, and appearance of real-world objects or environments and creating highly accurate digital replicas. It enables the conversion of physical objects into precise 3D models, which can be used for a wide range of applications.
How Does 3D Scanning Work?
3D scanning employs various technologies, such as laser scanning, structured light scanning, and photogrammetry, to capture the geometry and texture of objects. These scanners emit beams or project patterns onto the object’s surface, which are then recorded and processed into a digital model using specialized software.
Importance of Accuracy in 3D Scanning
Accurate 3D scanning is crucial for obtaining precise digital models. The level of accuracy depends on factors such as scanner resolution, calibration, and the complexity of the object being scanned. Higher accuracy ensures that the resulting models faithfully represent the physical objects, enabling reliable downstream applications.
Transforming the Architecture and Engineering Sector
Streamlining the Design and Prototyping Process
By using 3D scanning services, architects and engineers can efficiently capture existing structures or environments and convert them into digital models. These models serve as a foundation for designing modifications, additions, or entirely new structures, reducing errors and saving time in the design process.
Enhancing Building Information Modeling (BIM)
3D scanning plays a crucial role in creating comprehensive Building Information Models (BIM). By scanning existing structures and incorporating them into BIM software, architects, contractors, and project stakeholders gain a more accurate understanding of the building’s components, enabling better planning, coordination, and decision-making throughout the project lifecycle.
Preservation and Restoration of Historical Sites
3D scanning services are instrumental in preserving and restoring historical sites and monuments. By creating digital replicas of intricate architectural details or fragile artifacts, conservationists can analyze and document their condition, plan restoration efforts, and even recreate damaged or missing elements with precision.
Precise Documentation for Retrofitting Projects
When retrofitting existing structures, accurate documentation is essential. 3D scanning enables the creation of detailed as-built models that capture the current state of the structure, helping engineers identify potential clashes, plan modifications, and ensure a seamless integration of new elements.
Revolutionizing Healthcare and Medicine
Customized Prosthetics and Orthotics
3D scanning allows for the creation of customized prosthetic limbs and orthotic devices. By scanning the patient’s body or residual limb, healthcare professionals can design and fabricate personalized solutions that fit accurately and comfortably, improving the quality of life for individuals with limb loss or mobility impairments.
Surgical Planning and Training
Surgeons can use 3D scanning to capture a patient’s anatomy and generate precise 3D models for surgical planning. These models enable surgeons to visualize complex structures, simulate procedures, , and enhance surgical accuracy. Additionally, 3D-printed surgical guides and implants can be created based on the scanned data, facilitating precise and efficient interventions.
Dental and Orthodontic Applications
In dentistry, 3D scanning services are widely employed for various applications, including digital impressions, designing and manufacturing dental prosthetics (crowns, bridges, dentures), and orthodontic treatment planning. The non-invasive nature of 3D scanning provides patients with a more comfortable experience compared to traditional methods.
Advanced Medical Research and Development
Researchers and scientists leverage 3D scanning to create anatomically accurate models for medical education, training, and research purposes. It allows for the exploration of human anatomy in detail, the development of patient-specific simulations, and the testing of new medical devices or implants.
Advancing Manufacturing and Industrial Processes
Quality Control and Inspection
In manufacturing, 3D scanning plays a vital role in quality control and inspection processes. By comparing scanned objects with the original design specifications, manufacturers can identify defects, deviations, or inaccuracies early on, ensuring product quality and minimizing waste.
Reverse Engineering and Replication
3D scanning facilitates reverse engineering, enabling manufacturers to analyze and recreate existing products or components. By scanning an object, engineers can obtain accurate measurements and create a digital model, which can be used for redesign, optimization, or replication purposes.
Ergonomics and Human Factors Analysis
3D scanning helps improve product ergonomics and human-machine interaction. By scanning the human body, designers can evaluate and optimize product designs for comfort, safety, and usability, ensuring a better user experience and reducing the risk of musculoskeletal disorders.
3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping
The combination of 3D scanning and 3D printing technologies has revolutionized rapid prototyping. By scanning an object and converting it into a digital model, designers can quickly produce physical prototypes, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional prototyping methods.
Enriching the World of Entertainment and Media
Creation of Realistic Visual Effects
3D scanning services have become indispensable in the entertainment industry, particularly in film and video game production. By scanning actors, objects, or environments, digital artists can create realistic 3D models, textures, and animations, enhancing visual effects and immersing audiences in captivating virtual worlds.
3D Scanning for Gaming and Animation
In the realm of gaming and animation, 3D scanning allows for the creation of lifelike characters, props, and environments. By scanning real objects or using photogrammetry techniques, developers can incorporate accurate 3D assets into their projects, enhancing realism and improving the overall gaming or viewing experience.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) Experiences
3D scanning forms the foundation for immersive VR and AR experiences. By scanning physical spaces or objects and integrating them into virtual or augmented environments, developers can create highly realistic and interactive simulations, revolutionizing training, education, and entertainment.
Digital Preservation of Cultural Artifacts
Preserving cultural heritage is made easier with 3D scanning. By scanning and digitizing historical artifacts, artworks, or archaeological sites, experts can create virtual museums, archive fragile or inaccessible items, and facilitate research and educational initiatives, ensuring the preservation and accessibility of our shared heritage.
Accelerating Forensic Investigations
Crime Scene Documentation and Reconstruction
3D scanning enables precise documentation and reconstruction of crime scenes. By scanning the scene and capturing accurate measurements, forensic investigators can create detailed 3D models, aiding in crime scene analysis, evidence preservation, and courtroom presentations.
Facial Reconstruction and Identification
Facial reconstruction is an 6.2 Facial Reconstruction and Identification
Facial reconstruction is an essential tool in forensic investigations, and 3D scanning enhances its accuracy. By scanning skulls or skeletal remains, forensic anthropologists can create 3D models that assist in reconstructing facial features and potentially identifying unknown individuals.
Toolmark and Firearms Analysis
3D scanning is invaluable in toolmark and firearms analysis. By scanning and comparing toolmarks or firearm components, forensic experts can establish connections between evidence and potential sources, providing critical insights in criminal investigations.
Forensic Anthropology and Archaeology
In forensic anthropology and archaeology, 3D scanning aids in the documentation and analysis of skeletal remains, artifacts, and excavation sites. The ability to create accurate 3D models enhances research, facilitates comparative analyses, and contributes to the understanding of historical events or human remains.
Conclusion
As we have explored the diverse applications of 3D scanning services, it becomes evident that this technology is transforming industries in remarkable ways. From streamlining architectural design processes to revolutionizing healthcare, manufacturing, entertainment, and even forensic investigations, 3D scanning has become an indispensable tool.
With its ability to capture precise digital representations of physical objects, 3D scanning opens up new avenues for creativity, efficiency, and innovation.



