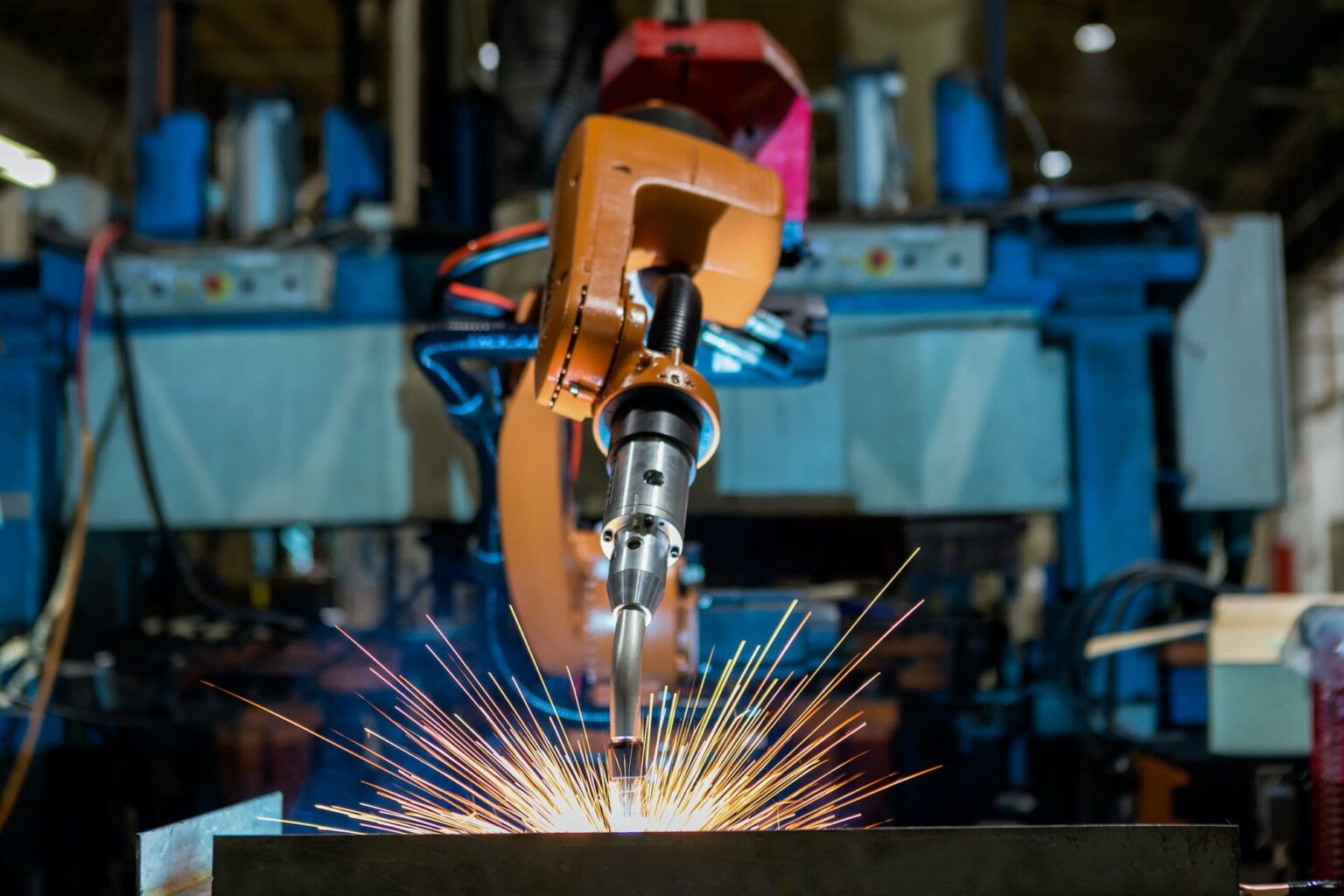

A review on robotic welding tasks
In robotic welding, tasks are automated using robots that handle and execute the weld based on software that can be reprogrammed to match the planned project.
Robotic welding is a massively advanced version of automated welding whereby robots execute the welds, but still, manual operators regulate and supervise the task. The deployment of robotic technology allows for fast and exact results, less waste, and more safety.
A welding robot arm can reach otherwise inaccessible areas and can perform intricate and exact welds more quickly compared to manual operators. This allows for more flexibility and saves on time during manufacturing.
With the range of machines accessible, robots can acclimatize to various welding tasks such as arc, laser, MIG, plasma, resistance, spot, and TIG welding. The main objective is to incorporate the ideal welding jigs and programs into the welding application.

How Does Robotic Welding Work?
When utilizing robots for any task, the approach needs adjusting to contain mechanization. The same applies to welding, which utilizes a couple of tools not present in its manual.
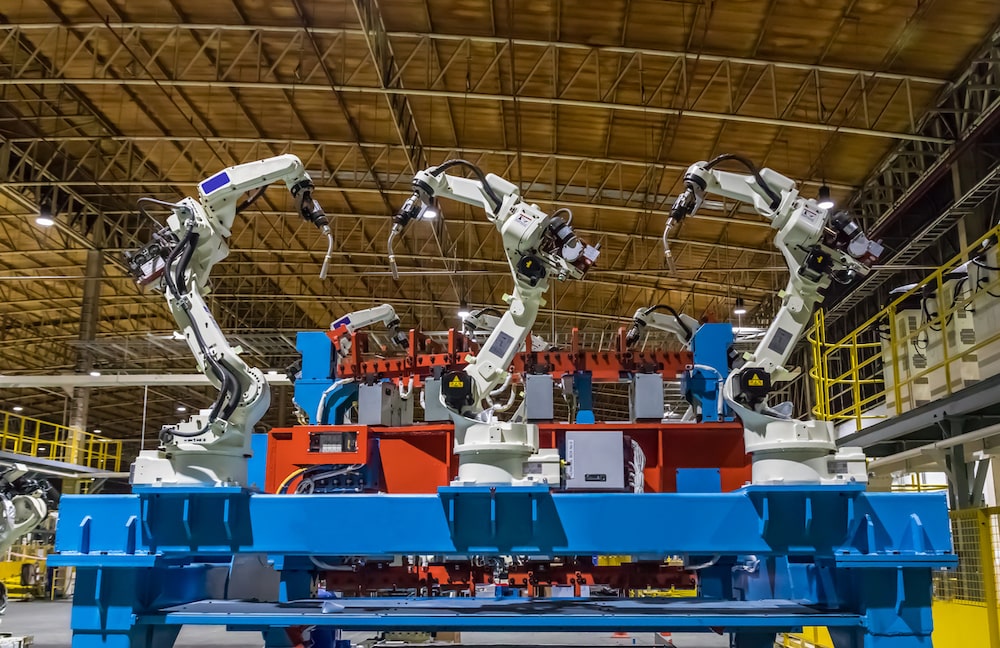
The machine itself has an arm that can rotate in three dimensions for rectilinear kinds and via more planes with articulating models. A wire feeder conveys the filler wire to the machine because it needs it for a welding task.
A high-heat torch at the end effector liquefies the metal allowing the welding task to happen. In such tasks, temperatures reach thousands of degrees hence why it’s better to deploy robots in order to keep manual operators safe.
However, manual operators still need to stay close to the machine. These operators need to have certification from the AWS (American Welding Society), which certifies not only manual welders but also robotic welding arm operators.
The operators configure the controller with a teach pendant. This is a device that sets new programs, moves the arm, and alters constraints for the task. The manual operator presses the switches on the control box to commence the weld.
The tool in the robotic arm heats to liquefy the metal and join the desired components. Next, a wire feeder conveys more metal cabling to the arm and torch. While waiting for the next pieces to join, the arm moves the torch to the cleaner to eliminate any splatters from it, which could stick and become part of the arm if not eliminated.
Since one of the key reasons to have robotic welding arms is to protect operators, these mechanized systems are equipped with several security features. Arc shields stop the high-heat arc from mixing with oxygen. Enclosed regions shield operators from light and high temps.
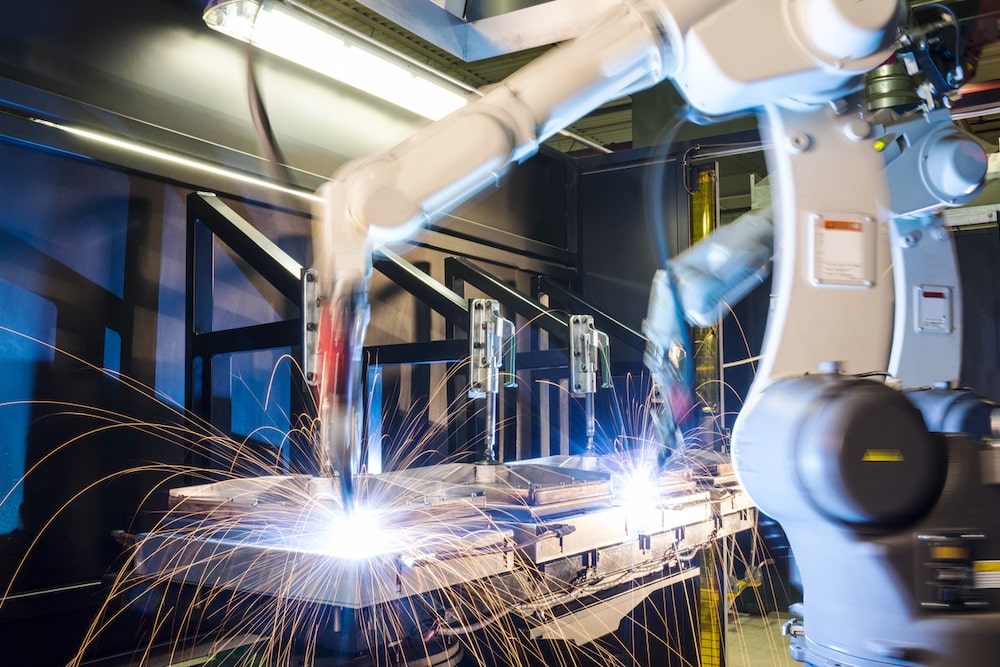

How Does Robotic Welding Compare to Manual Welding?
Manual welding still has a role to play in present-day manufacturing. However, manual welding is your best bet for projects requiring a pro to change the welding style used.
An expert welder can quickly change what he’s doing, but robots don’t acclimatize as quickly. However, since manual welding remains a procedure that many businesses need, likely, expert welders aren’t disappearing anytime soon.
In fact, with the shortage of pro welders, operators who have certification from the AWS can easily find jobs even with numerous businesses adopting welding robots.
Substituting manual operators for robots will not put the AWS out of business. Most welding operators need to have certification in the robotics side of this profession, for which they get certification from the AWS. Having manual operators who have a good understanding of welding ensures projects are programmed properly, thereby saving on costs.

Benefits of Robotic Welding
Enhanced Efficiency
Unlike manual operators who need breaks and time off, a robot can work twenty-four hours, seven days a week. More working hours and speed enable robotic welding arms to finish their tasks faster than manual operators. Thanks to faster finish times, the output of welding robots is much higher than anything manual operators can offer.
Enhanced Safety
Robotic welders are equipped with a variety of safety features to shield people from the welding arc, its luminosity, and high temperature.
These safety features allow for the work area to be safe. When operators work in a safe space, they will be more productive and have fewer complaints. In addition, damaged machinery and worker injuries are expensive for businesses, so these safety features also save them cash.
Less Delivery Charges
Once installed, machines can join a massive number of parts together. Though the upfront costs of acquiring a welding robot may be high, the massive productivity of the machine will ultimately make up for the high investment.
Since automatic welders have massive production levels, projects executed by them may cost less than having an entire team of manual operators.
Welding robots can also reduce delivery charges. The business executing welds can use one operator instead of an entire team to complete the same amount of work. As a result, the company you hire for welding can offer lower prices or more services by reducing overheads.
Less Waste
Due to their enhanced precision, robots produce less waste. Manual operators may need to throw away parts with weak welds or those wrongly welded together.
Since robots have a higher degree of precision, they commit fewer blunders. Without as much material wasted, a company that uses welding robots is more efficient.
More Accuracy
The appropriate project for a robot comprises repetitive movements applied to the massive volume of parts. Even the most experienced operator will ultimately commit blunders when included in this kind of work.
Robots will complete the project with more accuracy since the machine will continue working with the same level of attentiveness until the project is done.
Drawbacks of Robotic Welding
Less Flexibility
The advantage of robots working more precisely compared to manual operators also has a downside. Operators can respond to unforeseen situations in a manner that machines can’t.
When a welding robot needs to make an adjustment, the operator must halt the welding process and reprogram it. For intricate tasks, this increases the time needed to finish them.
Massive Upfront Costs
The delivery costs will most likely be lower when you use welding robots. However, if you were to invest in the machines and train operators yourself, you would probably find the venture a loss. In addition, companies that don’t professionally offer welding services may not utilize welding robots enough to justify the massive price of acquiring them.
Not Ideal for Small Projects
For smaller projects, the time required to program the robot can be longer than the welding task itself. A manual welder can complete the task faster for smaller projects, but it depends on the operator’s programming speed and project size.
Final Thought
As a result of their high productivity and time-saving benefits, welding robots have become vital in heavy and metal industries. These machines are best suited for brief welds with curved exteriors, which involve repetitive motions that don’t need continuous changes or shifts.



