Guiding Principles: Exploring Zakat and the Five Pillars of Islam
Introduction to Zakat and Five Pillars of Islam;
Zakat is one of the Five Pillars of Islam, which are the fundamental acts of worship and practice that every Muslim is required to follow. Zakat is an essential concept in Islamic teachings that focuses on charitable giving and social responsibility. It is a form of obligatory almsgiving aimed at helping those in need and fostering social and economic equity within the Muslim community.
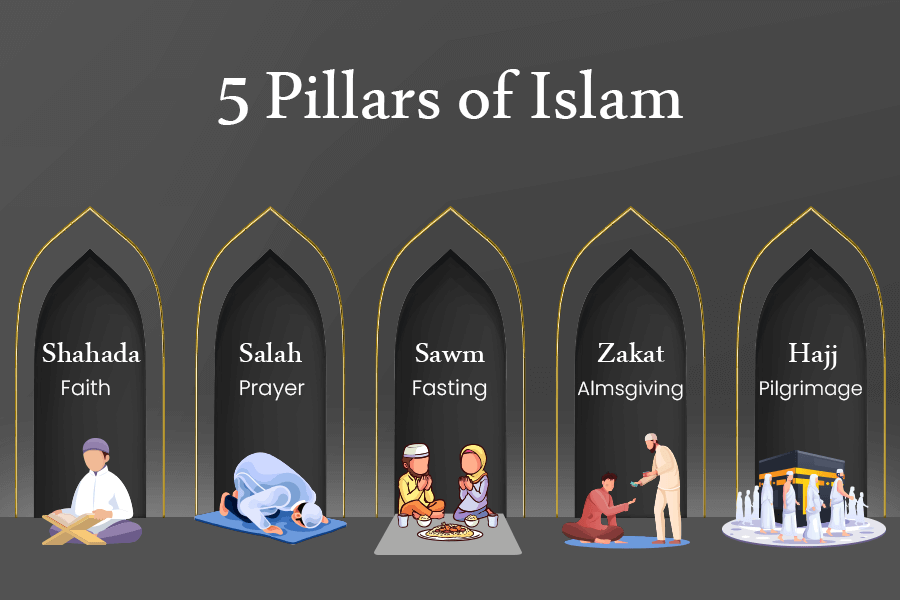
The Five Pillars of Islam: The Five Pillars of Islam are the core beliefs and practices that shape a Muslim’s faith and way of life. They provide a framework for spirituality, ethics, and community involvement. These pillars are:
- Shahada (Faith)
- Salat (Prayer
- Zakat (Charity)
- Sawm (Fasting)
- Hajj (Pilgrimage)
Importance of Zakat: Zakat holds a crucial place within the Five Pillars of Islam as it emphasizes the principle of sharing one’s wealth and resources with the less fortunate. It helps to address economic disparities, poverty, and inequality within the Muslim community. By fulfilling the obligation of Zakat, Muslims demonstrate their commitment to social justice and their responsibility to care for those in need.
In conclusion, the Five Pillars of Islam, including Zakat, serve as the foundation of a Muslim’s faith and practice. Zakat specifically highlights the importance of charity and social welfare, encouraging believers to actively participate in addressing the economic challenges faced by their community.
Concept of Wealth in Islam;
The concept of wealth in Islam is multifaceted and deeply rooted in the teachings of the religion. It goes beyond mere financial possessions and encompasses various dimensions, including responsibilities, attitudes, and ethical considerations. Here are some key aspects of the concept of wealth in Islam:
- Ownership and Stewardship: Islam recognizes that all material possessions ultimately belong to Allah, and humans are considered stewards or trustees of the wealth they possess. This understanding emphasizes the temporary nature of worldly possessions and encourages believers to use their wealth responsibly and ethically.
- Blessings and Gratitude: Wealth is seen as a blessing from Allah, and Muslims are encouraged to express gratitude for the provisions they have received. Gratitude is not just a personal sentiment; it should translate into actions that benefit others and honour the source of the blessings.
- Sharing and Charity: Islam places great emphasis on sharing one’s wealth with those in need. The practice of Zakat, a mandatory form of charity, highlights the obligation to provide for the less fortunate and promote economic justice within the community. Beyond Zakat, Muslims are encouraged to engage in voluntary acts of charity (sadaqah) to further assist those in need.
- Avoiding Excess and Wastefulness: Accumulating wealth for its own sake or engaging in extravagant consumption is discouraged in Islam. The religion promotes moderation and warns against wastefulness. Muslims are encouraged to strike a balance between meeting their needs and desires while also being mindful of the needs of others.
- Earning Wealth Ethically: Islam places great importance on earning wealth through lawful (halal) means and discourages engaging in dishonest or exploitative practices. Earning money through dishonesty, fraud, or exploitation of others is considered unethical and contrary to Islamic principles.
In summary, the concept of wealth in Islam is centred around the principles of stewardship, gratitude, sharing, ethical earning, and responsible use. It guides Muslims to strike a balance between their material and spiritual pursuits, with a strong emphasis on using wealth to benefit both oneself and the larger community while adhering to ethical and moral standards.
Zakat in Modern Society;
Zakat, as a fundamental pillar of Islam, holds enduring relevance in modern society, reflecting its timeless principles of social justice, compassion, and community welfare. In the context of today’s complex and interconnected world, the concept of Zakat offers valuable insights and solutions to address various socio-economic challenges.
In modern society, Zakat remains a potent tool for combating poverty and economic inequality. As wealth disparities continue to widen, Zakat provides a structured mechanism to redistribute resources from the affluent to the less fortunate. This practice resonates with the global pursuit of inclusive development, advocating for equitable distribution of wealth to uplift marginalized and vulnerable communities. By obligating individuals to share a portion of their wealth, Zakat fosters social cohesion and strengthens the sense of responsibility towards those who are economically disadvantaged.
Moreover, Zakat transcends national boundaries, making it particularly relevant in today’s globalized world. With the ease of communication and international cooperation, Muslims across regions can contribute to Zakat funds aimed at addressing humanitarian crises and developmental challenges around the world. This interconnectedness aligns with the increasing emphasis on global citizenship and solidarity, emphasizing our shared responsibility to alleviate suffering regardless of geographic or cultural differences.
In the contemporary economic landscape, Zakat also encourages ethical financial practices. The principle of earning wealth through lawful means (halal) and transparent transactions resonates with the call for corporate social responsibility and ethical business conduct. Zakat promotes financial transparency and accountability, aligning with modern demands for ethical finance and sustainable economic practices.
Furthermore, raising awareness about Zakat’s potential impact and fostering a culture of giving remains important endeavours. What is Zakat in Islam is a mandatory act of charitable giving, aimed at redistributing wealth and aiding those in need within the Muslim community. In a consumer-driven society, where materialism often prevails, promoting the spiritual and social benefits of Zakat can encourage Muslims to prioritize charitable giving over excessive consumption.
In conclusion, Zakat’s enduring significance in modern society lies in its ability to address contemporary challenges while upholding the timeless principles of Islam. Its potential to alleviate poverty, promote ethical financial practices, and foster global solidarity makes it a vital resource for building a more just and compassionate world. By embracing the essence of Zakat, individuals and societies can contribute to a more equitable and harmonious coexistence, aligning with the values of compassion and social responsibility.
Contemporary Relevance of the Five Pillars;
The 5 Pillars of Islam, despite originating over a millennium ago, maintain a profound contemporary relevance that resonates with the challenges and aspirations of modern society. These pillars provide a framework for personal spirituality, ethical conduct, community cohesion, and global citizenship, offering valuable insights for navigating the complexities of the modern world.
- Shahada (Faith): In a world characterized by diverse belief systems and ideologies, the declaration of faith remains relevant as a unifying principle. The affirmation of monotheism and the prophethood of Muhammad reinforce the value of recognizing common human roots and fostering mutual respect among individuals of different faiths. In a time of religious pluralism, the Shahada encourages dialogue, understanding, and peaceful coexistence.
- Salat (Prayer): The practice of regular prayers serves as a reminder of spiritual mindfulness amidst the fast-paced nature of modern life. In an era marked by stress and distraction, the discipline of daily prayers offers a moment of introspection, connection with the divine, and a reprieve from the demands of a busy world. Moreover, the collective Friday prayer (Jumu’ah) reinforces community bonds and shared spiritual experiences.
- Zakat (Charity): The imperative to share one’s wealth with those in need remains a potent response to contemporary economic inequalities. In a world grappling with wealth disparities and social injustice, Zakat promotes the redistribution of resources, encourages philanthropy, and supports social welfare initiatives. The emphasis on compassion and communal responsibility aligns with modern calls for inclusive development and social equity.
- Sawm (Fasting): Fasting during Ramadan offers modern individuals an opportunity for self-discipline, self-control, and empathy. As societies grapple with overconsumption and its environmental consequences, fasting encourages reflection on material desires and encourages sustainable practices. Additionally, fasting teaches patience and resilience, qualities vital for navigating the challenges of an interconnected and rapidly changing world.
- Hajj (Pilgrimage): The pilgrimage to Mecca reflects the global nature of Islam and the importance of unity among Muslims. In an age of easy travel and communication, the Hajj fosters cultural exchange, interfaith dialogue, and international cooperation. It reinforces the values of humility and equality, reminding individuals of their shared humanity regardless of nationality or background.
Overall, the Five Pillars offer a timeless ethical framework that addresses both personal development and societal well-being. Their contemporary relevance is highlighted by their alignment with current discussions on social justice, environmental sustainability, interfaith harmony, and global solidarity. By embracing the principles of the Five Pillars, individuals can navigate the challenges of the modern world while upholding the values of compassion, integrity, and community building.
Conclusion;
In conclusion, the Five Pillars of Islam stand as enduring pillars of guidance, offering profound wisdom and relevance in the context of both traditional and modern society. These foundational principles—Shahada, Salat, Zakat, Sawm, and Hajj—transcend time and culture, serving as a compass for Muslims to navigate the complexities of life with integrity, compassion, and a strong sense of purpose.
These Pillars provide a holistic framework that addresses not only individual spirituality but also the broader social fabric. They emphasize the importance of faith, mindfulness, generosity, self-discipline, and unity. Their teachings have the power to foster harmony within diverse communities, promote ethical conduct in personal and professional life, and inspire a commitment to social justice and global citizenship.
In today’s world, where technological advancements, globalization, and societal challenges have reshaped the way we live, the Five Pillars remain remarkably relevant. Their principles resonate with modern discussions on social equity, sustainable practices, interfaith dialogue, and shared responsibility. They encourage believers to strike a balance between the material and the spiritual, cultivating a sense of purpose and connection amidst the complexities of contemporary life.
Ultimately, the Five Pillars of Islam serve as a timeless guide, offering individuals a path to inner fulfilment and a framework for contributing positively to the betterment of society. By embracing these Pillars, individuals can strive for personal growth, ethical conduct, and social harmony, enriching their lives and the world around them with the values of faith, compassion, and unity.



