The Role of Vitamins in Supporting the Pineal Gland’s Function: A Comprehensive Review
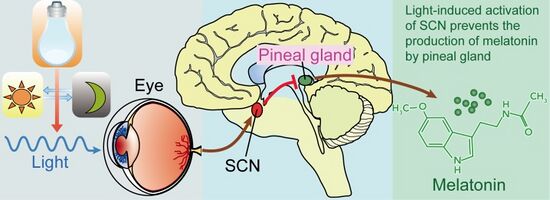
The Pineal gland vitamins, a small endocrine gland located in the brain, has long fascinated researchers due to its unique functions and potential influence on various physiological processes. One area of interest is the role of vitamins in supporting the pineal gland’s function. This article aims to provide a comprehensive review of the vitamins that may play a significant role in maintaining optimal pineal gland health and function.
Vitamin D and the Pineal Gland:
Vitamin D, often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is known for its role in calcium absorption and bone health. However, emerging evidence suggests that vitamin D may also impact the pineal gland. The presence of vitamin D receptors within the pineal gland suggests a potential regulatory role in melatonin synthesis. Melatonin, a hormone produced by the pineal gland, plays a crucial role in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Research suggests that vitamin D deficiency may disrupt melatonin production, leading to sleep disturbances and circadian rhythm disruption.
Vitamin B6 and Pineal Gland Function:
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is involved in various enzymatic reactions within the body. Studies have shown that vitamin B6 plays a critical role in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, including serotonin and dopamine. These neurotransmitters are closely linked to the pineal gland’s function, particularly in regulating mood, sleep, and overall well-being. Vitamin B6 deficiency has been associated with impaired melatonin production and disturbances in the sleep-wake cycle. Ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin B6 through diet or supplementation may support optimal pineal gland function.
Vitamin C and Pineal Gland Health:
Vitamin C, a potent antioxidant, is well-known for its immune-boosting properties. However, recent studies have indicated its potential role in maintaining pineal gland health. The pineal gland is highly susceptible to oxidative stress due to its high metabolic activity and exposure to various environmental toxins. Vitamin C’s antioxidant properties help neutralize harmful free radicals and protect the pineal gland from oxidative damage. Furthermore, vitamin C may support the conversion of serotonin to melatonin within the pineal gland, further enhancing its sleep-regulating functions.
Vitamin E and Pineal Gland Protection:
Vitamin E, a group of fat-soluble compounds with powerful antioxidant properties, has been studied for its potential neuroprotective effects. The pineal gland is particularly vulnerable to oxidative damage, and vitamin E’s antioxidant properties make it a crucial nutrient for maintaining pineal gland health. Additionally, vitamin E may enhance the synthesis and release of melatonin from the pineal gland, further promoting healthy sleep patterns. While more research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms, ensuring an adequate intake of vitamin E through diet or supplementation may help protect the pineal gland from oxidative stress and support its optimal functioning.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the pineal gland plays a crucial role in regulating various physiological processes, including sleep, mood, and overall well-being. While more research is needed, evidence suggests that certain vitamins, such as vitamin D, vitamin B6, vitamin C, and vitamin E, may support pineal gland health and function. Maintaining an adequate intake of these vitamins through a balanced diet or supplementation may help optimize the synthesis of melatonin, regulate circadian rhythms, and protect the pineal gland from oxidative damage. Further exploration of the relationship between vitamins and the pineal gland may contribute to our understanding of overall brain health and well-being.



