The Brain and Spinal Cord: Pillars of the Nervous System
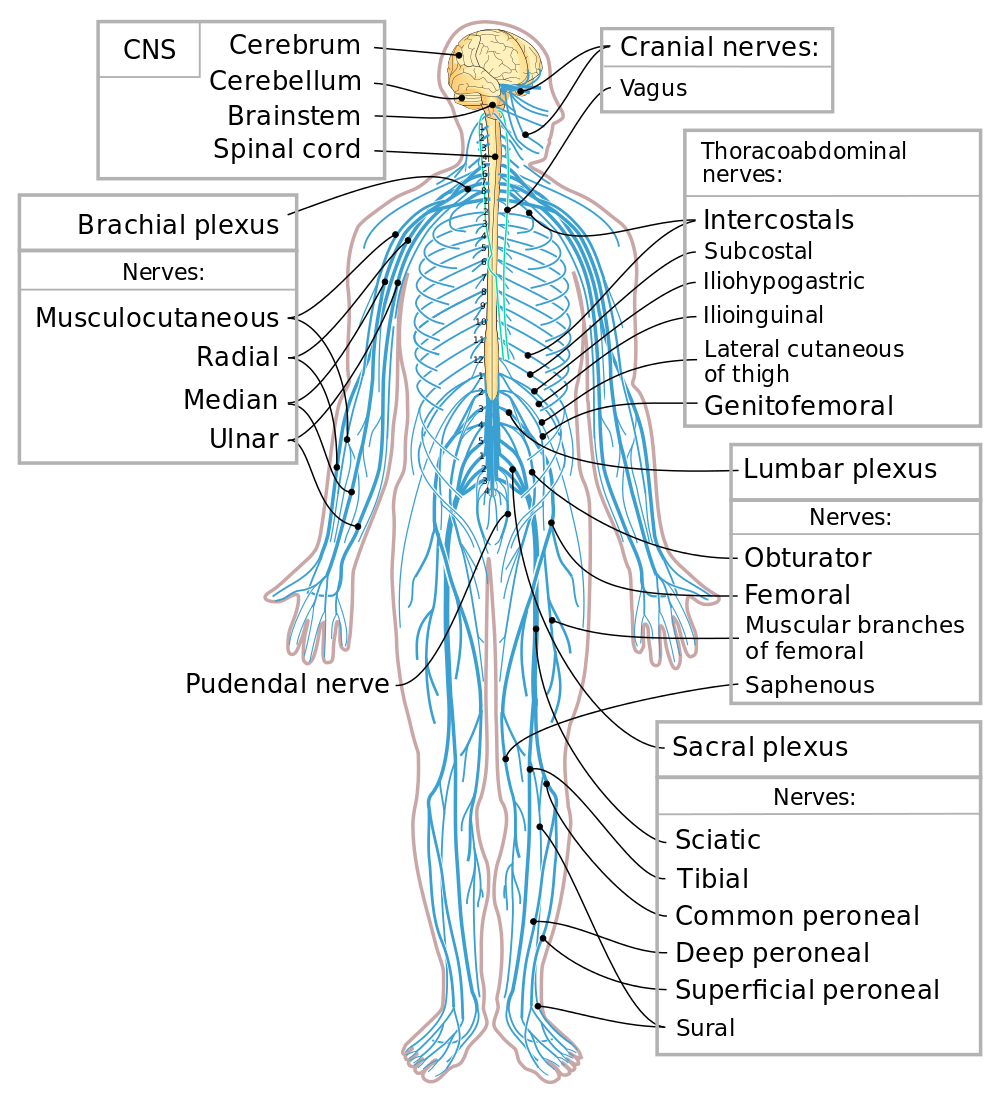
The human body is a complex and intricate system, with the brain and spinal cord being its central operational units. These components of the central nervous system (CNS) are crucial in controlling and coordinating various bodily functions. This article aims to provide a detailed understanding of the brain and spinal cord, their functions, and the significance of the vagus nerve in this system.
Anatomy and Function of the Brain
The brain, a marvel of the human body, is the control center of the entire nervous system. It is divided into several parts, each with specific functions. The cerebrum, the largest part, is responsible for cognitive functions such as thinking, reasoning, and memory. The cerebellum, located under the cerebrum, regulates motor movements, balance, and coordination. The brainstem, connecting the brain to the spinal cord, controls basic life functions like breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure.
The Spinal Cord: A Vital Conduit
The spinal cord, extending from the base of the brain down through the spine, acts as a critical conduit for transmitting signals between the brain and the rest of the body. It is composed of nerves that carry motor and sensory information, enabling movement, sensation, and reflex actions. The spinal cord is protected by the vertebral column, which also provides structural support to the body.
The Brain-Spinal Cord Connection
The seamless connection between the brain and spinal cord is vital for the CNS’s functioning. This connection allows for the rapid transmission of signals, facilitating quick responses to stimuli. Damage to this connection, as seen in spinal cord injuries or diseases like multiple sclerosis, can lead to significant functional impairments.
Role of the Vagus Nerve
The vagus nerve, part of the peripheral nervous system, extends from the brainstem to the abdomen. It plays a key role in the parasympathetic nervous system, often termed the “rest and digest” system. This nerve influences various functions, including heart rate, digestion, and mood regulation. It’s a prime example of the body’s intricate network, where the peripheral and central nervous systems interact.
Brain and Spinal Health Issues
Health issues affecting the brain and spinal cord can range from traumatic injuries to degenerative diseases. Brain disorders include stroke, traumatic brain injuries, and neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s. Spinal conditions include herniated discs, spinal stenosis, and spinal cord injuries. These conditions can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, requiring specialized medical care and rehabilitation.
Neurological Research and Advancements
Advancements in neurological research have led to a better understanding of the brain and spinal cord. This includes developments in neuroimaging techniques, which allow for detailed visualization of the CNS structures and are crucial in diagnosing various conditions. Research in neuroplasticity, the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new connections, is also providing insights into recovery after CNS injuries.
Neuroprotection and Rehabilitation
Neuroprotection strategies aim to preserve and protect the nervous system from damage. This includes the use of medications, surgical interventions, and lifestyle changes to mitigate the risk of neurological disorders. Rehabilitation, involving physical therapy, occupational therapy, and cognitive exercises, plays a crucial role in helping individuals recover from brain and spinal cord injuries.
The Future of CNS Healthcare
The future of CNS healthcare is promising, with ongoing research in stem cell therapy, neurore generation, and personalized medicine. These areas hold potential for revolutionary treatments for various neurological conditions, offering hope for improved outcomes and quality of life for those affected.
Conclusion
The brain and spinal cord are fundamental to the functioning of the human body, orchestrating a wide array of vital processes. Understanding their anatomy, functions, and the interconnected role of the vagus nerve is crucial in the field of healthcare. Continued advancements in research and treatment strategies are essential in addressing the challenges posed by brain and spinal health issues. As we progress in our understanding of these critical components of the CNS, the potential for improving patient care and outcomes continues to expand.



