Navigating Early Pregnancy: Understanding the Global Challenge of NIPT Awareness
Introduction:
In the complex landscape of prenatal care, expectant mothers are faced with a multitude of decisions aimed at ensuring the health and well-being of both themselves and their unborn child. Central to this journey are prenatal screening tests, which serve as crucial tools in identifying potential genetic disorders early on, enabling informed decisions and appropriate management. However, recent research has highlighted a concerning trend: a significant lack of awareness surrounding these tests, particularly Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT), among pregnant women worldwide.
The Study’s Revelation:
A recent study conducted at the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Mangalagiri, sheds light on the global issue of inadequate awareness surrounding prenatal screening tests, with a specific focus on NIPT. Published in [insert publication name/year], the study reveals that a substantial proportion of pregnant women, not limited to India alone, lack adequate knowledge about these tests. Among the 200 participants surveyed, a mere 36.5% demonstrated sufficient awareness, with only 7% showing familiarity with NIPT. These findings underscore a universal need for targeted educational initiatives to bridge the awareness gap and empower expectant mothers worldwide.
Understanding the Significance of NIPT:
NIPT stands out as a non-invasive alternative to traditional invasive procedures like amniocentesis, offering a safer method for detecting chromosomal abnormalities with high accuracy. By analyzing cell-free fetal DNA present in the maternal bloodstream, NIPT can identify conditions such as Down syndrome, Edwards syndrome, and Patau syndrome as early as 10 weeks into pregnancy. This early detection empowers expectant parents with valuable information to guide their future decisions regarding prenatal care and potential interventions.
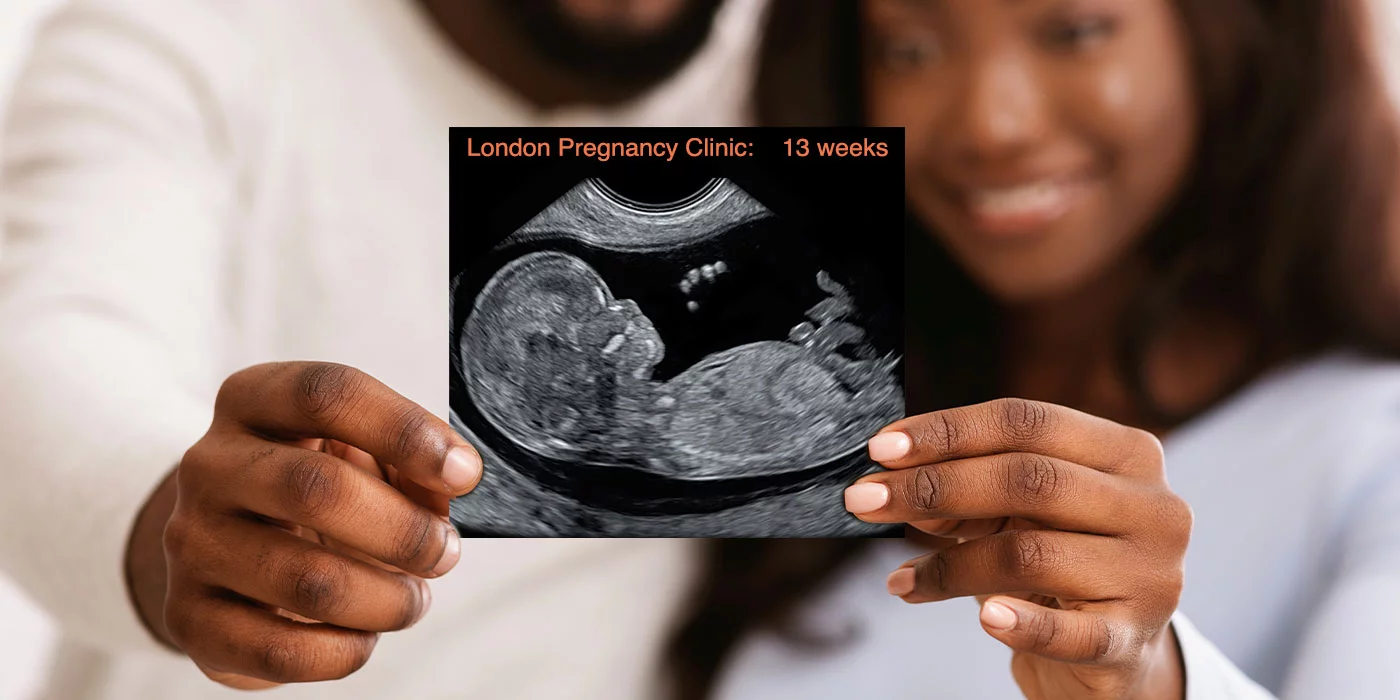
The Role of Early Pregnancy Scans:
Early pregnancy scans play a vital role in educating patients about the outcomes of NIPT. These scans, often conducted in the first trimester, provide expectant mothers with visual confirmation of their pregnancy and an opportunity to discuss prenatal screening options with their healthcare provider. Integrating information about NIPT into early pregnancy scans, like London Pregnancy Clinic, helps raise awareness about its importance and benefits, laying the foundation for informed decision-making throughout the pregnancy journey.
The Global Impact:
The lack of awareness surrounding NIPT and prenatal screening tests is not limited to any single region or country. Studies from various parts of the world have highlighted similar trends, emphasizing the need for a global response to address this pressing issue. Factors such as socio-cultural differences and disparities in healthcare systems contribute to variations in awareness levels, further emphasizing the need for tailored educational interventions on a global scale.
Addressing the Awareness Gap:
To tackle this global challenge, collaborative efforts involving healthcare providers, policymakers, and community organizations are imperative. Comprehensive educational campaigns should be developed and implemented across diverse platforms, including healthcare facilities, community centers, and digital channels. These initiatives must emphasize the benefits of early detection and informed decision-making in optimizing maternal and child health outcomes.
Furthermore, integrating prenatal education programs into existing maternal healthcare services can ensure widespread access to accurate information and support for expectant mothers worldwide. By empowering women with the knowledge they need to navigate their prenatal care effectively, these initiatives can facilitate proactive decision-making, alleviate anxiety, and enhance overall pregnancy experiences.
The Role of Healthcare Providers:
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in facilitating discussions about prenatal screening tests with their patients. Open and honest conversations tailored to the individual needs and preferences of expectant mothers can foster trust, alleviate concerns, and promote active engagement in the decision-making process. By serving as trusted sources of information and guidance, healthcare providers can empower pregnant women worldwide to advocate for their own health and the health of their unborn child.
Conclusion:
The findings of the study underscore the critical need for enhanced awareness of prenatal screening tests, including NIPT, among pregnant women worldwide. By addressing disparities in awareness and facilitating informed decision-making, we can strive towards improving maternal and child health outcomes on a global scale. Together, let us embark on a journey to empower expectant mothers with the knowledge and support they need to navigate the early stages of pregnancy with confidence and peace of mind, regardless of geographical location or socio-cultural background. Early pregnancy scans, integrated with information about NIPT, serve as valuable tools in educating patients and promoting informed decision-making throughout the pregnancy journey.



