
Taxpayer Identification Number
Learn what your taxpayer identification number is, when you need it, and how to obtain it.
The IRS uses a Taxpayer Identification Number (TIN) to administer tax laws. Taxpayer Identification Numbers include your Social Security Number (SSN), Individual Taxpayer Identification Number (ITIN), Employer Identification Number (EIN), Taxpayer Identification Number for Pending US Adoptions (ATIN), and Preparer Taxpayer Identification Number (PTIN).
TINs are issued by the IRS, except for your Social Security Number (SSN), which is used by the Social Security Administration (SSA).

When do I need my Taxpayer Identification Number?
A TIN needs to be included when filing your tax returns or claiming tax treaty benefits, and on other tax related documents. Additionally, a TIN must be included on a withholding certificate if the beneficial owner is claiming:
– Exemption from certain annuities
– Exemption for effectively connected income

How do I get a TIN?
To find out how to receive your Taxpayer Identification Number, including an ITIN, EIN, PTIN, ATIN, or SSN, read the information provided below:

ITIN:
To receive your ITIN complete IRS Form W-7, IRS Application for Individual Taxpayer Identification Number. Form W-7 requires evidence of your alien status and identity.
To submit your Form W-7 and relevant documentation, you can do one of the following:
- Mail Form W-7 and your documentation to the address shown in the Form W-7 instructions;
- Present your Form W-7 and documentation at an IRS walk in office;
- Process your application through an IRS authorized Acceptance Agent – entities such as colleges, financial institutions or accounting firms. These agents are authorized to assist ITIN applications and will forward your Form W-7 to the IRS for processing.

When applying for an ITIN, applicants must apply using the revised Form W-7 and attach a federal income tax return to the form. There is a ‘Form W-7 (SP)’ available for Spanish speakers. The IRS provides an Interactive Tax Assistant tool that helps you to determine whether you should file an application to receive an ITIN.
EIN:
Your Employer Identification Number (EIN) is used to identify a business entity, or by estates and trusts which have income that must be reported on Form 1041, US Income Tax Return for Estates and Trusts.
Foreign Persons/Entities claiming an EIN:
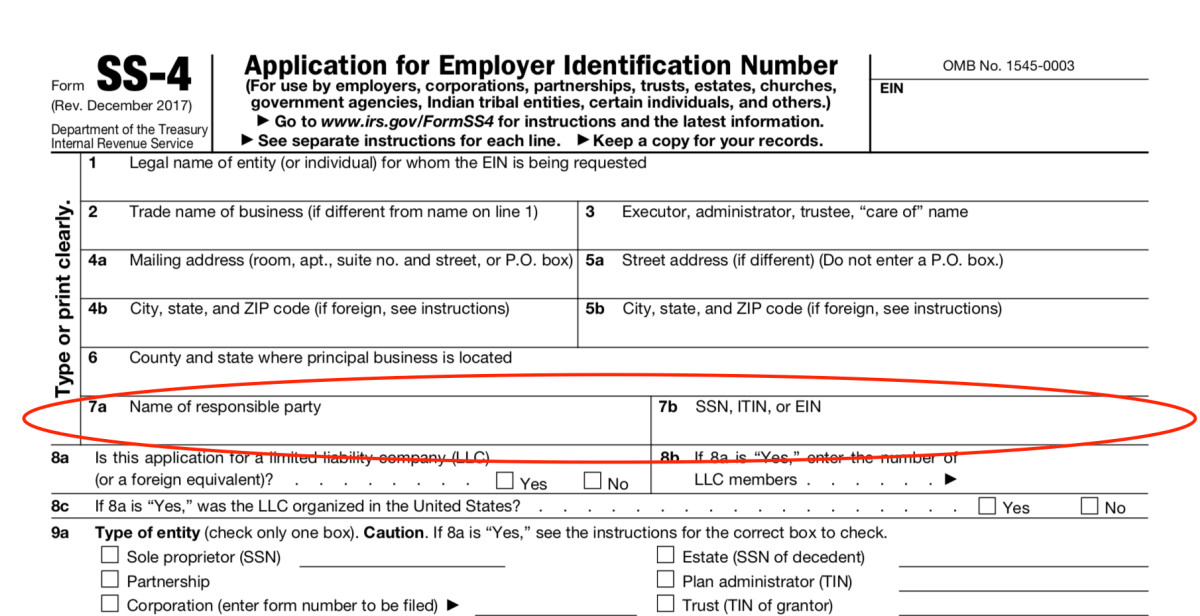
Foreign entities that are claiming exemption from withholding because of a tax treaty will need an EIN, and can obtain this by submitting Form SS-4, Application for Employer Identification Number to the IRS.
Foreign entities filing Form SS-4 only for the purpose of receiving an EIN to claim a tax treaty exemption, and otherwise have no US income or employment tax return filing requirements, should do the following:

- Write “N/A” on line 7b of Form SS-4, unless they already have an SSN or ITIN.
- Check the “other” block when answering question 10 on Form SS-4, and write immediately after it the most appropriate of the following phrases:
- “For W-BEN Purposes Only”
- “For Tax Treaty Purposes Only”
- “897(i) Election”
- “Required under Reg. 1”
- If you have no US tax return filing requirements and questions 11 to 17 do not apply, annotate with “N/A”.
PTIN:
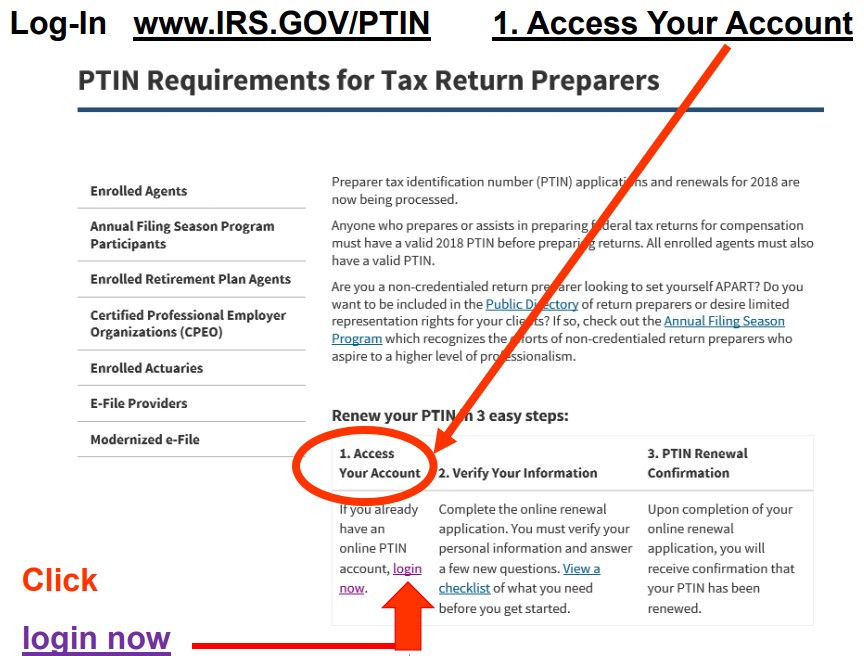
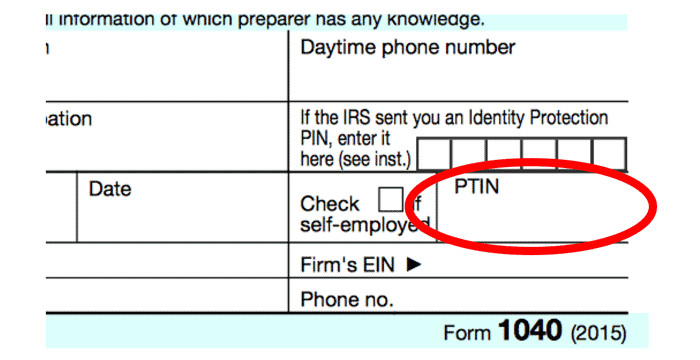
Since January 1, 2011, using a Preparer Tax Identification Number (PTIN) is no longer optional if you prepare all, or part of, any federal tax return or refund claim. To get your PTIN, you need to use the IRS’ new sign-up system. If you have a PTIN that you received before September 28, 2010, you must apply for a renewed PTIN using this new system and may receive the same number if all of your information matches what was on record.
Alternatively, if you don’t want to apply for a PTIN online, you can use Form W-12, IRS Paid Preparer Tax Identification Number Application. However, this takes 4-6 weeks to process.
ATIN:
An Adoption Taxpayer Identification Number (ATIN) is used for people who are legally adopting a US citizen or resident child but are unable to get an SSN for this child in time for filing their tax return.
An ATIN is a 9-digit number issued by the IRS, which is applied for with Form W-7A, Application for Taxpayer Identification Number for Pending US Adoptions. Do not apply with this form if the child being adopted is not a US citizen or resident.

SSN:
In order to receive your Social Security Number (SNN), you will need to complete Form SS-5, Application for a Social Security Card, and submit evidence of your identity, US citizenship or lawful alien status, and your age.
What is an SSN (Social Security Number) used for?
You will need to list the SSN of any dependent or spouse that you are claiming exemptions for on your income tax return. When a dependent or spouse does not have an SSN or is not eligible to get one, you will need to list their ITIN instead.

When is an ITIN used?
An ITIN is a tax processing number that is available to those who cannot get an SSN, including non-resident and resident aliens, their spouses and dependents. Your ITIN is a 9-digit number that is formatted like an SSN (NNN-NN-NNNN).
Do you need a TIN for children who were born and died in the same year?
You do not need to include an SSN or ITIN for dependent children who were born and died within the same year. Instead, attach a copy of their birth certificate and write Died on the appropriate exemption line on your tax return.



