How can we hide bald scalp
There are several ways to hide a bald scalp, ranging from temporary solutions to more permanent ones. Here are some options:
- Hairstyles:
- Longer Hair: Allowing your hair to grow longer can help cover bald spots. Longer hair can be styled to cover thinning areas.
- Layered Haircut: A layered haircut can add volume and texture, making hair appear thicker.
- Hair Products:
- Hair Fibers: These are tiny fibers that adhere to existing hair, making it appear thicker. They can be sprinkled onto the thinning areas and are usually undetectable once applied.
- Thickening Shampoos and Conditioners: These products can add volume to your hair, making it appear fuller.
- Hair Accessories:
- Hats and Caps: Wearing hats or caps can be a stylish way to cover a bald scalp, especially on days when you don’t want to bother with other solutions.
- Scarves and Head Wraps: These can be fashionable and functional, providing coverage for the scalp.
- Cosmetic Solutions:
- Hair Concealers: Similar to hair fibers, these are products that can be sprayed or applied to the scalp to create the illusion of thicker hair.
- Scalp Micropigmentation (SMP): This is a semi-permanent cosmetic tattoo that mimics the appearance of hair follicles on the scalp. It can create the illusion of a closely shaved head or add density to thinning areas.
- Medical Interventions:
- Hair Transplant: This is a surgical procedure where hair follicles are transplanted from one part of the scalp (or body) to the balding area.
- Topical Medications: Some medications, such as minoxidil, are designed to promote hair growth and may be applied directly to the scalp.
- Wigs and Hairpieces:
- Wigs: A wig is a full head covering that can completely conceal a bald scalp. Modern wigs come in various styles and materials, and many are very natural-looking.
- Hairpieces: These are smaller than wigs and are designed to cover specific areas of hair loss.
It’s important to choose a solution that fits your preferences, lifestyle, and budget. Consulting with a hairstylist, dermatologist, or a specialist in hair restoration can provide personalized advice based on your specific situation.
What are the medical treatments for bald scalp?
Several medical treatments are available for addressing baldness or hair loss. These treatments aim to either stimulate hair growth, slow down hair loss, or restore the appearance of a fuller head of hair. It’s important to note that the effectiveness of these treatments can vary from person to person, and results may take time. Here are some common medical treatments for a bald scalp:
- Minoxidil (Rogaine): This is an over-the-counter topical medication that is applied directly to the scalp. Minoxidil is thought to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. It is available in both liquid and foam formulations and is often used for treating male and female pattern baldness. Results may take several months, and continuous use is typically required.
- Finasteride (Propecia): This prescription medication is taken orally and is specifically for men. Finasteride works by inhibiting the action of the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which is associated with hair loss. It is most effective for treating male pattern baldness. As with minoxidil, results may take several months, and continuous use is necessary.
- Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy: In this procedure, a small amount of the patient’s blood is drawn, processed to concentrate the platelets, and then injected into the scalp. The growth factors in platelets are believed to stimulate hair follicles and promote hair growth. PRP therapy is used for both male and female pattern baldness.
- Low-Level Laser Therapy (LLLT): LLLT involves the use of red light lasers or LED devices to stimulate hair follicles and encourage hair growth. It can be administered through laser caps, combs, or helmets. The mechanism of action is not fully understood, but some studies suggest it may have a positive impact on hair growth.
- Hair Transplant Surgery: Hair transplantation involves the surgical removal of hair follicles from a donor area (usually the back or sides of the scalp) and their transplantation to the bald or thinning areas. This is a more invasive and permanent solution for hair restoration.
- Corticosteroid Injections: In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be used to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune response in the scalp. This can be particularly useful for conditions such as alopecia areata.
- Dutasteride: Similar to finasteride, dutasteride is an oral prescription medication that inhibits DHT. It is not yet FDA-approved for treating hair loss, but it is sometimes used off-label.
Before pursuing any medical treatment, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist who specializes in hair loss. They can assess your specific situation, recommend appropriate treatments, and discuss potential side effects and expectations. Additionally, individual responses to treatments can vary, so what works for one person may not work as well for another.
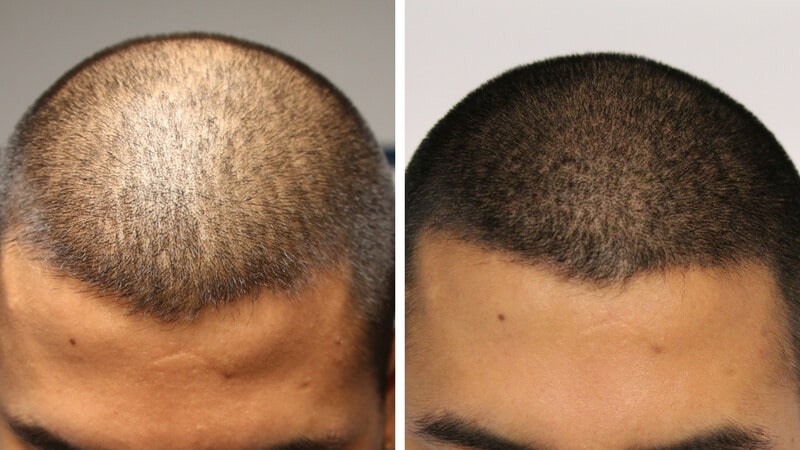
Hair transplant surgery
Hair transplant surgery is a cosmetic procedure designed to address hair loss or baldness. It involves moving hair follicles from one part of the body (usually the back or sides of the scalp, where hair is resistant to balding) to areas with thinning or no hair. The most common types of hair transplant procedures are follicular unit transplantation (FUT) and follicular unit extraction (FUE).
Hair density treatment is a non-surgical approach to combat hair thinning and loss. It typically includes various therapies, like laser treatments, topical medications, and platelet-rich plasma therapy. These treatments aim to improve hair thickness and overall scalp health.
Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT):
- Donor Area Preparation:
- A strip of skin is surgically removed from the donor area (typically the back or sides of the scalp).
- The donor area is then sutured or stapled to close the wound.
- Graft Preparation:
- The strip of skin is dissected into individual follicular units under a microscope.
- These follicular units contain one to four hairs each.
- Recipient Site Preparation:
- Tiny incisions are made in the recipient area (the bald or thinning area where the transplants will be placed).
- Graft Placement:
- The prepared follicular units are carefully placed into the recipient sites.
Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE):
- Donor Area Shaving:
- The donor area is trimmed to expose the individual hair follicles.
- Extraction:
- Individual follicular units are extracted one at a time using a small punch tool.
- These units are typically extracted from a wider area compared to FUT.
- Recipient Site Preparation:
- Like in FUT, tiny incisions are made in the recipient area.
- Graft Placement:
- The extracted follicular units are then implanted into the recipient sites.
Recovery and Results:
- Recovery Time:
- Patients may experience some swelling, discomfort, and redness in both the donor and recipient areas.
- Healing time varies, but most people can return to their normal activities within a week.
- Results:
- Initially, the transplanted hair may fall out, but new hair should start growing within a few months.
- Full results may take up to a year or more to become apparent.
Considerations:
- Natural-Looking Results:
- A skilled surgeon can create natural-looking results by considering factors such as hairline design and the angle and direction of hair growth.
- Permanent Solution:
- Transplanted hair is typically resistant to the factors that cause pattern baldness, making the results long-lasting.
- Cost:
- Hair transplant surgery can be expensive, and the cost may vary based on factors such as the surgeon’s experience, the extent of baldness, and the chosen technique.
- Suitability:
- Not everyone is a suitable candidate for hair transplant surgery. Factors such as the extent of hair loss, the availability of donor hair, and overall health play a role in determining candidacy.
It’s essential to consult with a qualified and experienced hair transplant surgeon to discuss your specific situation, expectations, and potential risks. They can provide personalized advice and help you make an informed decision about whether a hair transplant is the right option for you.



